Ligand docking is a computational method of determining how a drug-like small molecule (the ligand) interacts with a protein of interest. The Meiler lab leverages its expertise in RosettaLigand and other small molecule docking techniques to be able to accurately predict the structure of small molecule protein interactions. This structure-based knowledge of allows us to better understand how drugs bind to their target receptors, such as how the binding of modulators of GPCR receptors can affect the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, and can assist in the discovery of new drugs for these conditions.
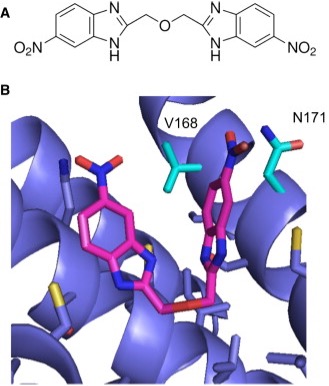
Figure: Ligand docking can be used to predict the interaction of drug like molecule (such as the molecule shown in A) to a protein. B) By optimizing the predicted interaction in silico, the best conformation and location of the ligand (magenta sticks) within the protein binding pocket (blue) can be found. Structural data, such as interactions with particular residues (e.g. V168 and N171), can then be used to inform further experiments (such as mutations) or to propose different ligands which may function better. (Figure from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.)
References:
[1]Schüß C, Vu O, Schubert M, Du Y, Mishra NM, Tough IR, Stichel J, Weaver CD, Emmitte KA, Cox HM, Meiler J, Beck-Sickinger AG. Highly Selective Y4 Receptor Antagonist Binds in an Allosteric Binding Pocket. J Med Chem. 2021 Mar 11;64(5):2801-2814. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02000. Epub 2021 Feb 17. PMID: 33595306.
[2]Yang Z, Han S, Keller M, Kaiser A, Bender BJ, Bosse M, Burkert K, Kögler LM, Wifling D, Bernhardt G, Plank N, Littmann T, Schmidt P, Yi C, Li B, Ye S, Zhang R, Xu B, Larhammar D, Stevens RC, Huster D, Meiler J, Zhao Q, Beck-Sickinger AG, Buschauer A, Wu B. Structural basis of ligand binding modes at the neuropeptide Y Y1 receptor. Nature. 2018 Apr;556(7702):520-524. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0046-x. Epub 2018 Apr 18. PMID: 29670288; PMCID: PMC5920736.
[3]Sánchez-Soto M, Casadó-Anguera V, Yano H, Bender BJ, Cai NS, Moreno E, Canela EI, Cortés A, Meiler J, Casadó V, Ferré S. α2A- and α2C-Adrenoceptors as Potential Targets for Dopamine and Dopamine Receptor Ligands. Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Nov;55(11):8438-8454. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1004-1. Epub 2018 Mar 18. PMID: 29552726; PMCID: PMC6143434.
[4]Swale DR, Sheehan JH, Banerjee S, Husni AS, Nguyen TT, Meiler J, Denton JS. Computational and functional analyses of a small-molecule binding site in ROMK. Biophys J. 2015 Mar 10;108(5):1094-103. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.01.022. PMID: 25762321; PMCID: PMC4375722.
[5]Gregory KJ, Nguyen ED, Malosh C, Mendenhall JL, Zic JZ, Bates BS, Noetzel MJ, Squire EF, Turner EM, Rook JM, Emmitte KA, Stauffer SR, Lindsley CW, Meiler J, Conn PJ. Identification of specific ligand-receptor interactions that govern binding and cooperativity of diverse modulators to a common metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 allosteric site. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Apr 16;5(4):282-95. doi: 10.1021/cn400225x. Epub 2014 Feb 26. PMID: 24528109; PMCID: PMC3990945.
